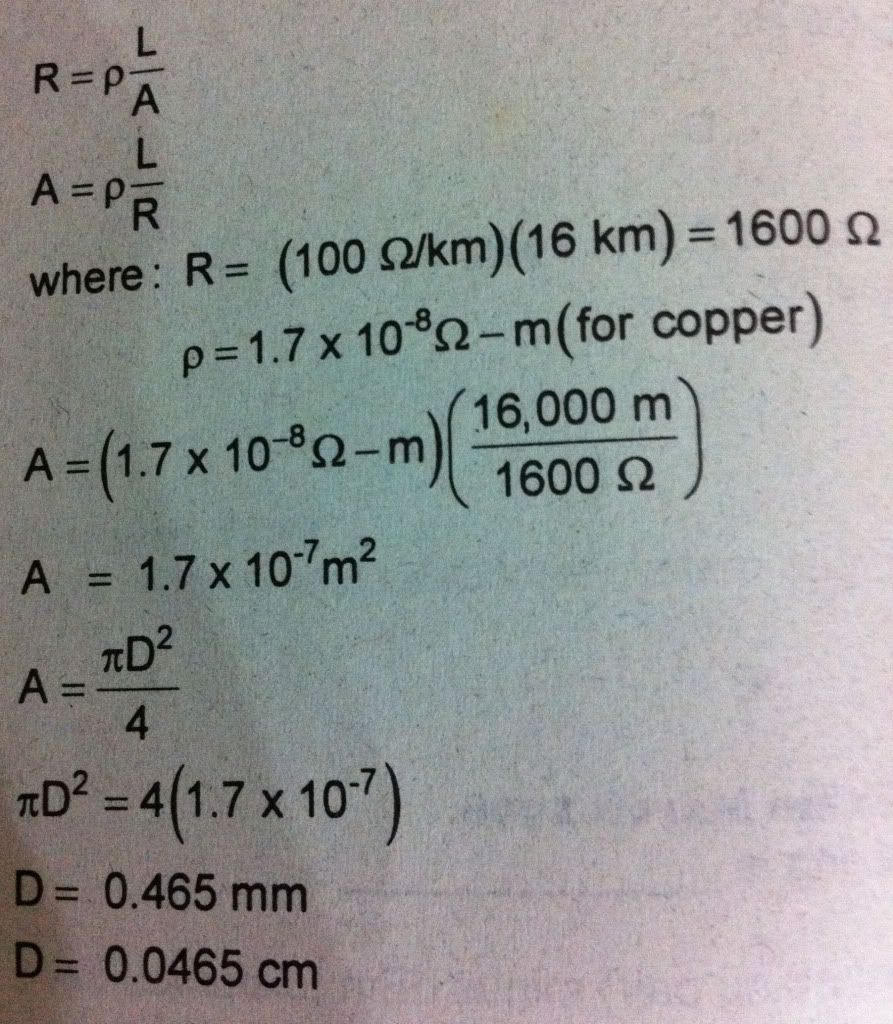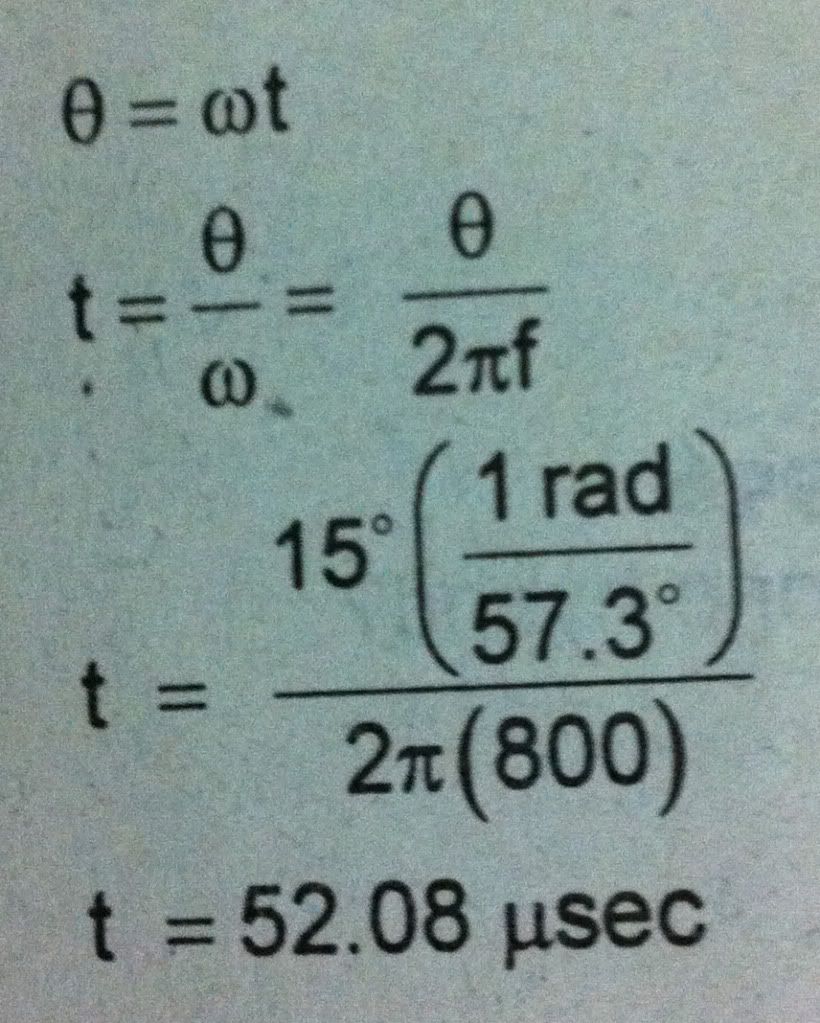ECE Board
Exam April 2001
A duration
of traffic path occupancy from a call, sometimes referred to as an average
duration of occupancy of one or more path from calls.
Holding time
ECE Board
Exam November 2000
Frequency
band where Total Access Communication System (TACS) is allocated.
935-960 MHz; 890-915 MHz
ECE Board
Exam April 2000
Referred as
the forward link channel of the cellular duplex system
Cell to mobile unit
ECE Board
Exam November 1999
This
referred to a condition in a telephone network where the calling party cannot
get connected to the party being called
Blocked call
ECE Board
Exam April 1999
One of the
components of a basic cellular system that handles the billing activities of
the network.
Mobile telephone switching office
ECE Board
Exam November 1998
Refers to a
continuous tone generated in a local exchange terminal through a combination of
two frequencies 350 Hz and 440 Hz
Call waiting tone
ECE Board
Exam April 1998
A multiple
access technique used in GSM cellular system.
TDMA
ECE Board
Exam November 1997
What
signal-to-noise ratio is required for satisfactory telephone services?
30 dB
ECE Board
Exam April 1997
What is the
advantage of sidetone?
Assures that the telephone is working
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
A special
device circuit connecting two private branch exchanges (PBX).
Tie trunk
ECE Board
Exam March 1996
The
modulation system used for telegraphy is
Frequency shift keying
ECE Board
Exam Board April 2001
Describe as
the signal-to-noise ratio required to meet a satisfactory telephone service
30 dB
ECE Board
Exam November 2000
Which of the
following system uses frequency band 870-890 MHz as a transmit band of its base
station?
Advanced Mobile Phone Service AMPS
ECE Board
Exam April 2000
What third
symbol in emission designation indicates cellular voice transmission?
E
ECE Board
Exam November 1999
A term for a
conventional land telephone line which is attached to the local telephone
exchange by a pair of twisted copper wires.
Fixed wire
ECE Board Exam
April 1999
A mobile
telephone system, which used analogue cellular radio standard which was
superceded by the Advanced Mobile Phone System in the US.
IMTS
ECE Board
Exam November 1998
Refers to
the duration occupancy period of call during its use.
Holding time
ECE Board
Exam April 1998
How wide is
the spectrum bandwidth of a single GSM carrier?
200 kHz
ECE Board
Exam November 1997
The standard
deviation of the variation in the transmission loss of a circuit should not
exceed
1 dB
ECE Board
Exam April 1997
One (1)
Erlang is equal to ________.
36 CCS
ECE Board
Exam April 2001
A type of
call where cell cannot receive the supervisory audio tones in 5 seconds causing
the cell site to turn the cell transceiver.
Call drop
ECE Board
Exam November 2000
Telephone
channel has a band-pass characteristics occupying the frequency range of ______
300 – 3400 Hz
ECE Board
Exam April 2000
A digital
mobile telephone system which called a European derivative of a Global System
for Mobile Communication System operating at a higher frequency band.
DCS-1800
ECE Board
Exam 1999
The receiving
and transmission of printed materials over the telephone wires.
Facsimile
ECE Board
Exam April 1999
One of the
following central office switching equipment resistance limits refers to the
longest subscriber loop length.
2000 ohms
ECE Board
Exam April 1998
The modulation
technique used by GSM cellular system
Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying
ECE Board
Exam November 1997
Nominal
voice channel
4 kHz
ECE Board
Exam April 1997
Transmission
of printed material over telephone lines
Facsimile
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
What is the
transmission rate of a GSM cellular system?
270 kbps
ECE Board
Exam March 1996
A device to
be connected across the headset in telephone receivers to reduce the effects of
acoustic shock.
Two rectifiers in parallel with opposite
polarities
ECE Board
Exam April 2001
The signal
quality of the cells is constantly monitored by the base station, when the
quality of the calls drops below a certain specified level, the base request
the MTSO to try and find a better cell site is referred as _________.
Hand – off
ECE Board
Exam November 2000
In mobile
communication such as the cellular service, the current maximum power is rated
at __________
3 watts
ECE Board
Exam April 2000
A special
tone frequency which is transmitted by the mobile unit to cell site signaling
call termination.
10 kHz
ECE Board
Exam November 1999
This is the Nordic
analogue mobile radio telephone system originally used in Scandinavia.
NMT
ECE Board
Exam April 1999
An analogue
mobile telephone system which was designed for United Kingdowm using 900 MHz
frequency band.
TACS
ECE Board
Exam April 1998
An interfering
current in a telegraph or signaling channel due to telegraph or signaling
current by another channel.
Cross fire
ECE Board
Exam November 1997
What is the
channel bandwidth of a standard analogue telephone system?
300 – 3400 Hz
ECE Board
Exam April 1997
1 – CCS is
equal to
100
ECE Board
Exam March 1996
Crosstalk
coupling is ___________
dBm (disturbing pair) minus dBm (disturbed
pair).
the difference between readings on a cable
pair with a tone and a cable pair without tone read at the far end of the cable.
signals from one circuit that get into
another circuit
ECE Board
Exam April 2001
Process of
automatically changing frequencies as the mobile unit transfer into a different
frequency zones so that the conversation can be continued in the new zone
without redialing.
Hand-off
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
What is the
diameter of a copper wire to be used in a 16 km loop with a dc loop resistance
of 100 ohms/km?
ECE Board
Exam April 2001
Process of
automatically changing frequencies as the mobile unit transfer into a different
frequency zone so that the conversation can be continued in the new zone
without redialing.
Hand-off
ECE Board
Exam November 2000
A stage in cellular
communication where voice channel is assigned to link up a call connection
after a mobile or network originated a call.
Call completion
ECE Board
Exam November 1999
How much
approximate maximum power can a human voice possibly produce?
1 milliwatt
ECE Board
Exam April 1999
A transmission
facility connecting points 1 and 2 which is either permanent or temporary,
normally voice grade facility provided by a public network provider.
Channel
ECE Board
Exam April 1998
Best described
as an amplifier used in radio telephony.
Class C
ECE Board
Exam November 1997
Refers to
the first generation of local loop system in telecommunication technology
Analogue cellular
ECE Board
Exam April 1997
1 Erlang is
____________
1 TU
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
Combination of
modulator, channel and detector.
Discrete channel
ECE Board
Exam March 1996
The local
loop of the telephone system is understood to be
A two-wire or four-wire communication
circuit between the customer’s premise and the central office.
ECE Board
Exam November 1997
Refers to
the first generation of local loop system in telecommunication technology
Analogue cellular
ECE Board
Exam April 1997
_________ is
used to measure speech volume
Volume unit meter
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
What component
in the telephone set has the primary function of interfacing the handset to the
local loop?
Induction coil
ECE Board
Exam March 1996
The ______
filter attenuates signals but passes frequencies below and above that band.
Band stop
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
____________
is out-of-bound signaling between toll central offices (Bell System Standard)
3700 Hz
ECE Board
Exam March 1996
In a
telephone system, the customer’s telephone directory numbering is from 000 to
999, what is the capacity of the system?
1,000 lines
ECE Board
Exam April 2001
How much
signal-to-noise ratio is required to attain a satisfactory local exchange
network?
35 dB
ECE Board
Exam April 2000
What is the
channel bandwidth of a standard analog telephone system?
300-3400 kHz
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
A voice
grade circuit using the PTN has an ideal passband of
0 to 4 kHz
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
What kind of
receiver is used in conventional telephone handset?
Electromagnetic
ECE Board
Exam April 2001
In telecommunications
the acronym NAM stands for
Numeric assignment module
ECE Board
Exam November 2000
Referred as
the reverse link channel of the cellular duplex system.
Mobile unit to cell
ECE Board
Exam April 2000
Provides interface
between the mobile telephone switching office and the mobile units
Cell site
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
What is the
power loss of a telephone hybrid?
3 Db
ECE Board
Exam April 2001
This is
small radio transceiver communication device which is normally wall mounted and
where the WLL subscriber plugs its telephone handset.
Telephone wireless terminal
ECE Board
Exam April 2000
A term used
in wireless telegraphy and telephony to counter irregular disturbing radiation
due to various causes which is produced by arc transmitter causing a rushing
sound in receiving telephones.
Mush
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
What is the
phase delay of an 800 Hz voice signal if the phase shift is 15 deg.?
ECE Board
Exam November 1996
A digital
identification associated with a cellular system
SIM
ECE Board
Exam April 2001
Component of
a basic cellular system that provides interface between the switching office
and the mobile units.
Cell site
Cell site
ECE Board
Exam November 2000
Which of the
following cellular system is the only system allowed inside United States?
AMPS
ECE Board
Exam April 2000
Which of the
following system uses frequency band 825 – 845 MHz as a receive band of it base
station?
Advanced Mobile Phone Services (AMPS)